Understanding Thoracic Pain Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Thoracic pain syndrome (TPS) is a condition that affects many individuals, often leading to significant discomfort and functional limitations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of thoracic pain syndrome, including its causes, symptoms, and the most effective treatment options available. Whether you're experiencing these symptoms personally or you're a healthcare professional looking to expand your knowledge, this guide will equip you with valuable insights.
What is Thoracic Pain Syndrome?
Thoracic pain syndrome is characterized by pain and discomfort in the thoracic region of the spine, which includes the middle part of the back. It can arise from various underlying conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders, nerve impingement, or inflammatory diseases. The thoracic spine consists of twelve vertebrae, and issues in this area can lead to referred pain in other parts of the body.
Common Causes of Thoracic Pain Syndrome
Understanding the root causes of thoracic pain syndrome is crucial for effective management. Below are some of the most common causes:
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion or improper lifting techniques can lead to muscle strain in the thoracic region.
- Herniated Discs: Disks that bulge or rupture can compress nearby nerves, resulting in pain.
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of the joints in the thoracic spine can cause inflammation and pain.
- Postural Issues: Poor posture, particularly in sedentary occupations, can lead to muscle fatigue and pain.
- Injuries: Trauma from accidents or falls can directly impact the thoracic region.
- Referred Pain: Conditions impacting the lungs, heart, or digestive system can manifest as thoracic pain.
Identifying the Symptoms of Thoracic Pain Syndrome
Symptoms of thoracic pain syndrome can vary widely among individuals. However, some common signs include:
- Localized Pain: Patients often report pain that is localized to the mid-back region.
- Radiating Pain: Discomfort may radiate to the shoulders, neck, or even down the arms.
- Stiffness: Many individuals experience stiffness, particularly after periods of inactivity.
- Tingling or Numbness: Nerve irritation can lead to sensations such as tingling or numbness.
- Difficulty Breathing: In severe cases, pain may exacerbate breathing difficulties.
Who is at Risk for Thoracic Pain Syndrome?
While thoracic pain syndrome can affect anyone, certain populations may be at a higher risk. These include:
- Athletes: High levels of physical activity and potential for injury increase risk.
- Office Workers: Prolonged sitting and poor ergonomics may contribute to the development of TPS.
- Older Adults: Age-related wear and tear on the spine can lead to conditions that cause thoracic pain.
- Individuals with Chronic Conditions: Certain health issues, such as arthritis or obesity, can predispose individuals to TPS.
Diagnosis of Thoracic Pain Syndrome
Accurate diagnosis of thoracic pain syndrome is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals typically utilize the following methods:
- Physical Exam: A thorough physical examination helps assess pain location, range of motion, and any neurological deficits.
- Medical History Review: Evaluating a patient's medical history can reveal underlying conditions contributing to TPS.
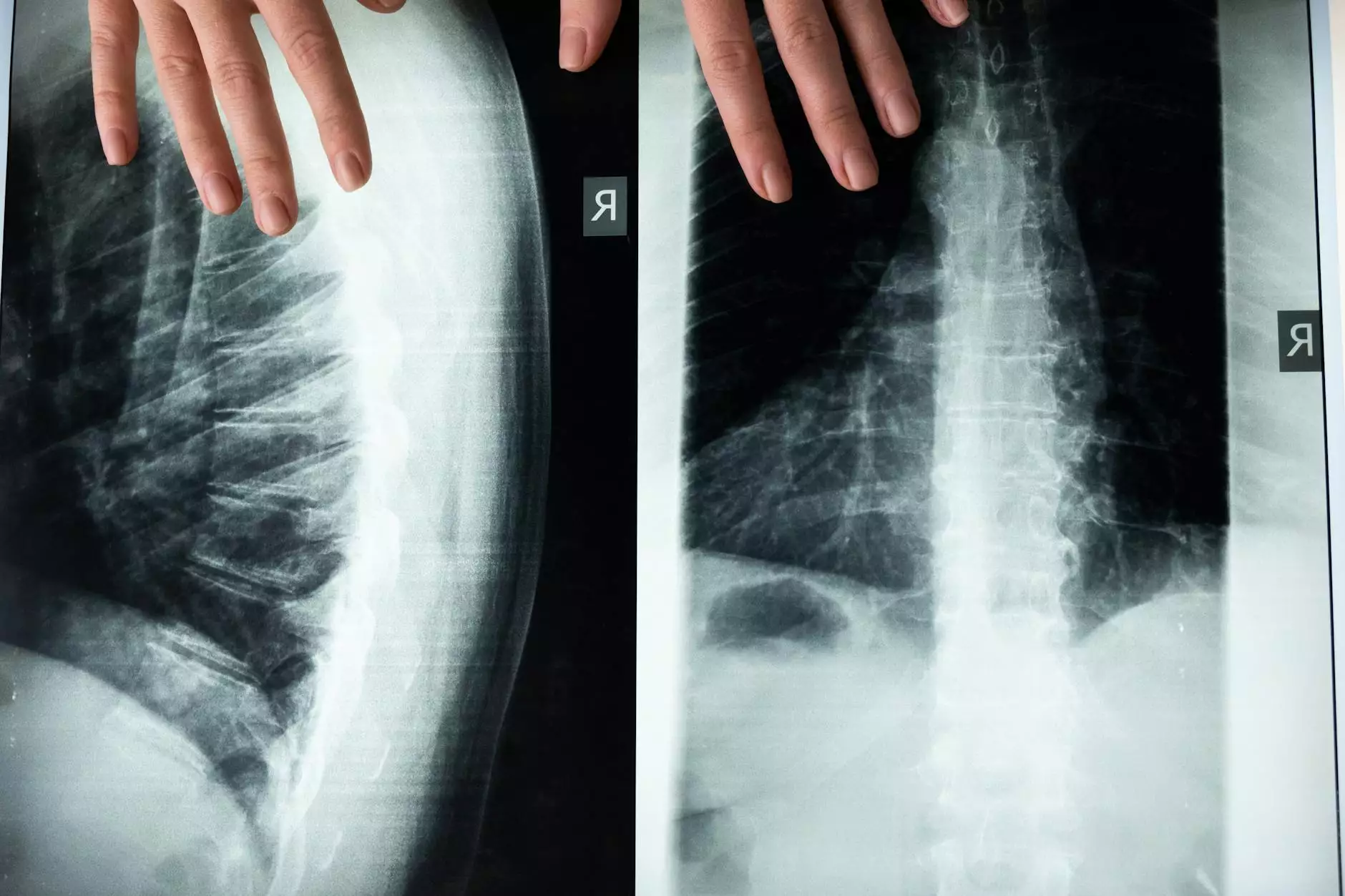
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be conducted to visualize the thoracic spine and identify problems.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test assesses nerve function and can help determine if nerve compression is present.
Treatment Options for Thoracic Pain Syndrome
Treating thoracic pain syndrome effectively often requires a multi-faceted approach. Treatment options can be categorized as follows:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense against thoracic pain syndrome:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and stretches can help improve strength, flexibility, and posture.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments can realign the spine and reduce pain.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and pain relievers can provide symptom relief.
- Hot/Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain temporarily.
- Postural Training: Ergonomic assessments and training on proper body mechanics can prevent recurrence.
2. Surgical Treatments
In cases where conservative methods fail, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Discectomy: Removal of herniated disc material to relieve nerve compression.
- Laminectomy: Surgical removal of the lamina to access the spinal cord and relieve pressure.
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves joining two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
3. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals seek complementary therapies to support their treatment. These may include:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice can help release tension and promote healing.
- Yoga and Mindfulness: Incorporating gentle yoga and stress-reduction techniques can enhance recovery.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can alleviate muscle tension and promote relaxation.
Living with Thoracic Pain Syndrome
Managing thoracic pain syndrome often requires ongoing lifestyle adjustments. Here are some strategies that can promote a better quality of life:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can strengthen the back muscles.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce strain on the spine and alleviate pain.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensure that workspaces are set up to promote good posture and reduce the risk of injury.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practices such as meditation and deep breathing can help manage pain perception.
- Support Networks: Connecting with support groups can provide valuable emotional support and practical strategies for coping.
Conclusion
Thoracic pain syndrome is a challenging condition that can impact daily life significantly. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. Whether you are experiencing thoracic pain yourself or helping someone who is, remember that comprehensive care—including physical therapy, chiropractic adjustments, and lifestyle changes—can lead to improved outcomes and enhanced well-being.
Additional Resources
For further information and support on thoracic pain syndrome, please visit iaom-us.com, a website dedicated to helping individuals manage their health and well-being through educational resources and expert guidance.